Hydroponics pH Guide: Importance, Meters & Adjustments
Hydroponics Made Easy: What is pH and Why Does It Matter for Your Plants?
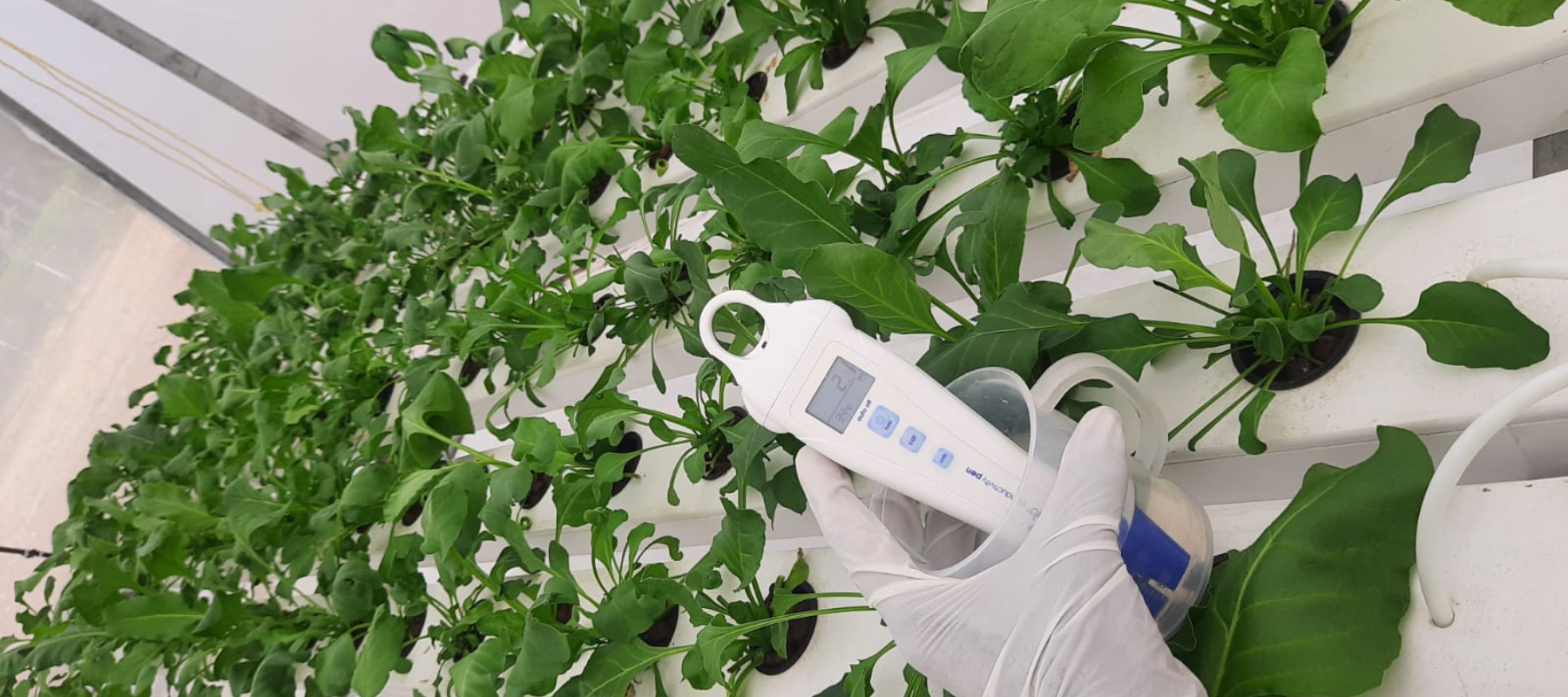

The art of growing without soil—hydroponics—is gaining in popularity as an efficient, sustainable, and space-saving method. If you are growing leafy greens on your kitchen window ledge, or running a mature indoor garden — pH is one thing you need to get your head around. Let's break down what pH is, why it’s essential, and how you can manage it effectively in your hydroponic setup.
What is pH?
Have you ever wondered why some hydroponic growers get so excited about pH? You know what it’s like, getting started with hydroponics and pH might seem overwhelming. But here's the thing: Following rules doesn't mean that you understand pH, it is about speaking your plants' language and giving them exactly what they need to thrive. pH is a measure of how acidic or alkaline a solution is, on a scale of 0 to 14:
- 0-6.9: Acidic
- 7: Neutral
- 7.1-14: Alkaline
In hydroponics, the pH has a direct effect on how well your plants will absorb nutrients. Even the most nutrient-rich solution is impossible for your plants to use at a pH that is too high or too low. When the pH is off balance, even if you have a nutrient-rich solution, your plants will not benefit from it.
It’s like your plant's comfort zone for pH. Plants are similar to you in the sense that you can have your room at a certain temperature, and similarly, plants can have an ideal pH range that they like 'just right' in.
However, the scale may seem straightforward, but small changes in pH can be big problems for your plant. Say a pH of 6.5 vs 5.5 doesn’t sound like much but to your lettuce or tomatoes that might be the difference in the world.
Why Does pH Matter for Hydroponics?
Imagine you’re at a restaurant, where a door locks all the delicious food behind. When your pH is off that’s essentially what happens, the nutrients are there, but your plants can't access them. Think of it like a door to the kitchen, when you get the pH right, you’re letting your plants feast like opening that wide door. Plants rely on specific pH ranges to absorb essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Here’s why it matters:
- Optimal Nutrient Uptake: Many plants grow well in the pH range of about 5.5 to 6.5. Here, nutrients dissolve perfectly in water, so that plants can easily absorb them. If pH is too high or too low nutrients such as iron, manganese, and zinc are especially prone to becoming unabsorbable.
- Prevents Nutrient Lockout: Nutrient lockout occurs on plants outside the ideal pH range, even though these nutrients are present in solution; they are no longer available to the plant. This can lead to deficiencies, stunted growth, and even death in the plant if left uncorrected.
- Healthier Plants: A balanced pH is essential for vigorous growth, resistance to disease, and higher yields. Plants with a balanced pH throughout will develop strong roots, lush foliage, and robust fruiting or flowering.
- Cost Efficiency: By proper control of pH you avoid wasting nutrients and keep your system working correctly. If your nutrients get absorbed efficiently then you will not need to change or adjust your solution as often and spend less time and less money.
Common Hydroponic Plants and Their pH Ranges
Here’s a quick reference chart to help you maintain the right pH for various plants. Different plants have different preferences, so if you’re growing multiple crops in one system, aim for a middle ground to accommodate all.
- Lettuce: 5.5 - 6.0 (likes it slightly more acidic)
- Tomatoes: 5.5 - 6.5 (pretty flexible)
- Spinach: 6.0 - 7.0 (can handle slightly higher pH)
- Strawberries: 5.5 - 6.5
- Basil: 5.5 - 6.5 (great starter plant)
- Cucumbers: 5.5 - 6.0
- Bell Peppers: 6.0 - 6.5
Growing multiple plants? Don't panic! Most plants thrive well in a middle ground of a pH near 6.0.
Tools You Need to Manage pH
Managing pH doesn’t have to be complicated. Below we have discussed and listed the tools you’ll need:
1. pH Meter
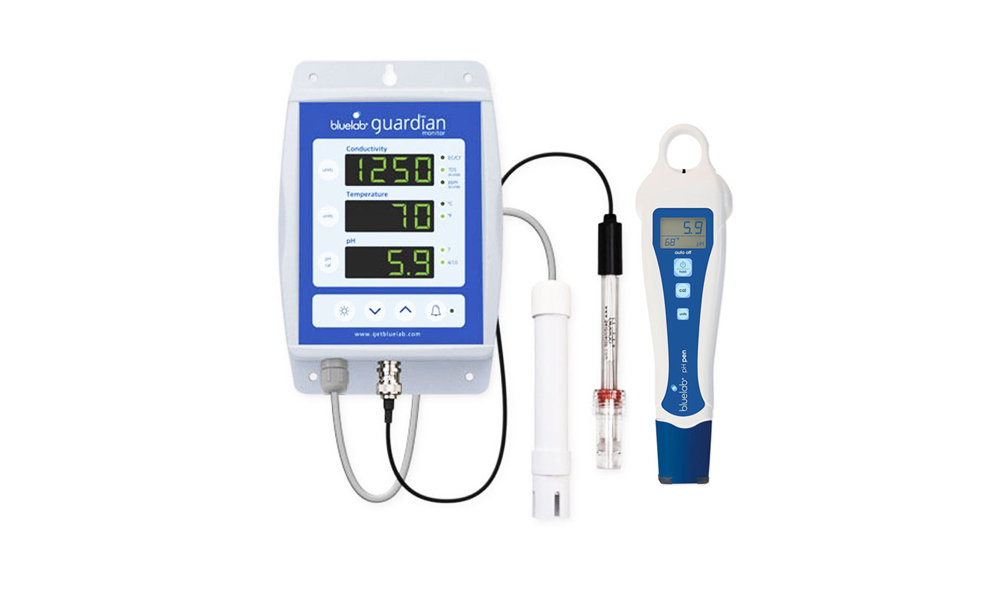
The pH meter is a crucial pH tester because you need an accurate reading. We need to look for a reliable, easy-to-calibrate model. Advanced meters often have temperature compensation, ensuring more accurate results.
2. pH Test Strips
pH test strips are a budget-friendly pH tester option. However, these are less accurate than a digital meter and are great for quick checks but may not be ideal for precise adjustments.
3. pH Up and pH Down Solutions

These are liquid additives that are added to your nutrient solution to get the pH adjusted. Tip: Be sure not to use household alternatives as there might be impurities.

Store your pH meter electrodes in a proper storage solution to keep your results accurate. By failing to do this, performance can be degraded and reading can be inaccurate.
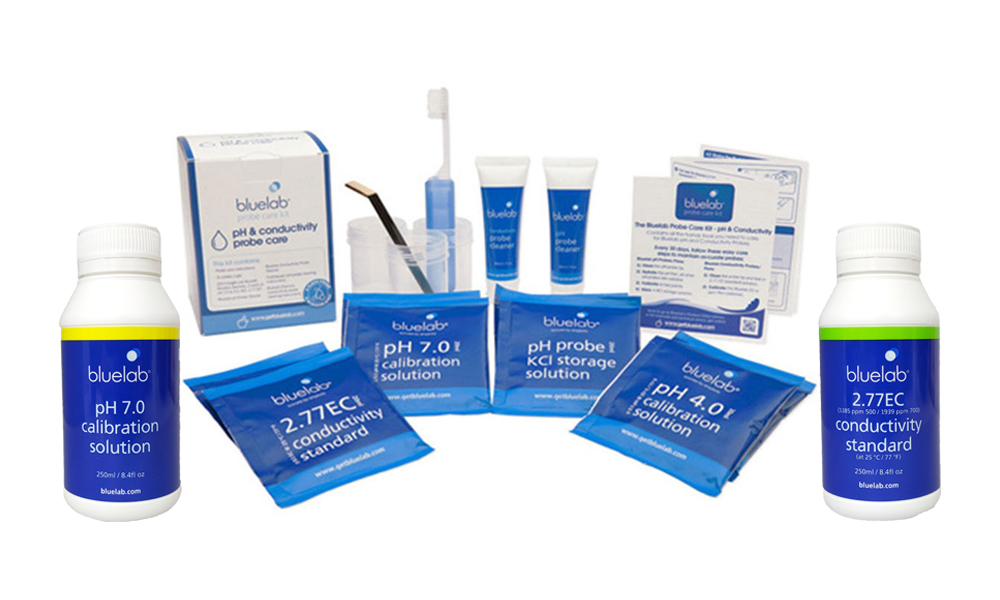
Use these standard solutions to regularly calibrate your pH meter. Skipping calibration can result in incorrect adjustment and plant stress.
Step-by-Step Guide to Managing pH in Hydroponics
You might have been overwhelmed by the details and the plethora of information above. However, keeping your pH in the optimal range is easier than you think. Follow these steps:
1. Prepare Your Nutrient Solution
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and mix your nutrient solution. Make sure you use clean room temperature water.
- Allow the solution to stabilize for a few minutes before testing the pH.
2. Measure the pH
- Use your pH meter or pH tester test strips to measure the solution’s pH.
- Have your pH meter calibrated so you get accurate readings. You should also calibrate weekly, or when you are suspicious that it is inaccurate.
3. Adjust the pH
- If the pH is too high, add a small amount of pH Down solution.
- If the pH is too low, add a small amount of pH Up solution.
- Till you reach the right range, re-check and stir thoroughly. Adjust slowly to always avoid overshooting your target.
4. Monitor Regularly
- Test the pH daily or at least every other day to get readings before pH deviations occur. Swings can be caused by changes in temperature, water evaporation, and plant uptake.
- Make adjustments as needed to maintain consistency.
5. Clean Your Tools
- Rinse your pH meter and all your tools after every use, as it prolongs their life and gives you the most accurate reading. When nutrients are added to the solution unchecked, residue can interfere with the measurement.
Tips for Maintaining Stable pH
- Start with Quality Water: Reverse osmosis and Distilled water will purify your water to minimise pH changes from impurities. Some minerals found in hard water will make the pH unstable.
- Keep It Simple: Don’t overcomplicate your nutrient mix as too many add-ins can destabilise pH. Follow trusted hydroponics formulas.
- Use a Reservoir: The larger water reservoir enables it to buffer those pH changes so that they need adjustment less frequently than would a smaller water reservoir.
- Track Trends: Write down some pH readings into a log, for example, find patterns, take corrective actions, log, and do it all again. This will work best for combating your problems before they grow big.
- Invest in Automation: It is well known that larger systems will require automatic pH monitoring and adjustments, and a pH controller is a good choice for this. An upfront cost may be higher, but doing so can save you time and effort in the long run.
- Beware of Drift: Problems caused by plant uptake and evaporation can result in a pH change over time.
Additional Tips for Beginners
- Test the Source Water: Before adding nutrients, test your source water’s pH. This gives you a baseline and helps with accurate adjustments.
- Don’t Overthink It: While pH management is important, it’s not rocket science. Follow the basics, stay consistent, and you’ll be fine.
- Join Communities: Online forums and local hydroponic groups are excellent places to learn and share experiences.
- Start Small: Begin with one or two plants to get the hang of pH management before expanding your system.
- Learn from Mistakes: It’s normal to make adjustments as you go. Keep experimenting and note what works best for your setup.
Final Thoughts
Understanding and managing pH is essential for hydroponics. Although it might seem intimidating at first, maintaining the right pH is simple and worth it. With the right tools, and with regular monitoring, and some patience, your hydroponic garden is going to thrive.
A little effort will pay off now and save you time and headaches later. So grab a pH meter, roll up your sleeves, and dive into the world of hydroponics with confidence. Happy growing up!



